Goal
This tutorial shows you:
- How to write attributes?
- How to read attributes?
- Note
- Although attributes can be associated with groups and datasets, only attributes with the root group are implemented in OpenCV. Supported attribute types are
int, double, cv::String and cv::InputArray (only for continuous arrays).
Source Code
The following code demonstrates reading and writing attributes inside the root group with data types cv::Mat, cv::String, int and double.
You can download the code from here or find it in the file modules/hdf/samples/read_write_attributes.cpp of the opencv_contrib source code library.
#include <iostream>
static void read_write_attributes()
{
String filename =
"attributes.h5";
String attr_mat_name =
"array attribute";
if (!h5io->atexists(attr_mat_name))
h5io->atwrite(attr_mat, attr_mat_name);
String attr_str_name =
"string attribute";
String attr_str =
"Hello HDF5 from OpenCV!";
if (!h5io->atexists(attr_str_name))
h5io->atwrite(attr_str, attr_str_name);
String attr_int_name =
"int attribute";
int attr_int = 123456;
if (!h5io->atexists(attr_int_name))
h5io->atwrite(attr_int, attr_int_name);
String attr_double_name =
"double attribute";
double attr_double = 45678.123;
if (!h5io->atexists(attr_double_name))
h5io->atwrite(attr_double, attr_double_name);
int expected_attr_int;
double expected_attr_double;
h5io->atread(&expected_attr_str, attr_str_name);
h5io->atread(expected_attr_mat, attr_mat_name);
h5io->atread(&expected_attr_int, attr_int_name);
h5io->atread(&expected_attr_double, attr_double_name);
CV_Assert(attr_str.compare(expected_attr_str) == 0);
CV_Assert(fabs(attr_double - expected_attr_double) < 1e-10);
h5io->close();
}
{
read_write_attributes();
return 0;
}
Explanation
The first step is to open the HDF5 file:
Then we use cv::hdf::HDF5::atwrite() to write attributes by specifying its value and name:
String attr_mat_name =
"array attribute";
if (!h5io->atexists(attr_mat_name))
h5io->atwrite(attr_mat, attr_mat_name);
- Warning
- Before writing an attribute, we have to make sure that the attribute does not exist using cv::hdf::HDF5::atexists().
To read an attribute, we use cv::hdf::HDF5::atread() by specifying the attribute name
h5io->atread(expected_attr_mat, attr_mat_name);
In the end, we have to close the HDF file
Results
Figure 1 and Figure 2 give the results visualized using the tool HDFView.

Figure 1: Attributes of the root group
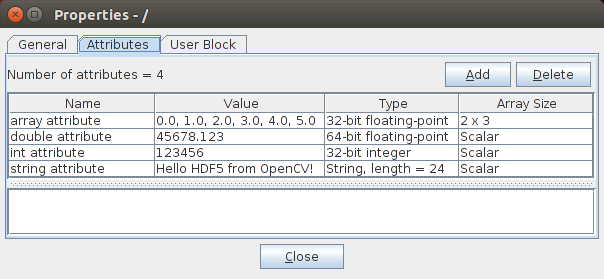
Figure 2: Detailed attribute information



