What is the most common way to debug computer vision applications? Usually the answer is temporary, hacked together, custom code that must be removed from the code for release compilation.
If the program is compiled without visual debugging (see CMakeLists.txt below) the only result is some information printed to the command line. We want to demonstrate how much debugging or development functionality is added by just a few lines of cvv commands.
11 #define CVVISUAL_DEBUGMODE 21 template<
class T> std::string toString(
const T& p_arg)
34 printf(
"usage: cvv_demo [-r WxH]\n");
35 printf(
"-h print this help\n");
36 printf(
"-r WxH change resolution to width W and height H\n");
41 main(
int argc,
char** argv)
47 "{ help h usage ? | | show this message }" 48 "{ resolution r |0x0| resolution to width and height in the format WxH }";
50 string res(parser.get<
string>(
"resolution"));
51 if (parser.has(
"help")) {
58 if (sscanf(res.c_str(),
"%d%c%d", &resolution->
width, &dummych, &resolution->
height) != 3) {
59 cout << res <<
" not a valid resolution" << endl;
66 if (!capture.isOpened()) {
67 std::cout <<
"Could not open VideoCapture" << std::endl;
72 printf(
"Setting resolution to %dx%d\n", resolution->
width, resolution->
height);
80 std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> prevKeypoints;
83 int maxFeatureCount = 500;
84 Ptr<ORB> detector = ORB::create(maxFeatureCount);
88 for (
int imgId = 0; imgId < 10; imgId++) {
92 printf(
"%d: image captured\n", imgId);
94 std::string imgIdString{
"imgRead"};
95 imgIdString += toString(imgId);
104 std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> keypoints;
107 printf(
"%d: detected %zd keypoints\n", imgId, keypoints.size());
110 if (!prevImgGray.
empty()) {
111 std::vector<cv::DMatch> matches;
112 matcher.
match(prevDescriptors, descriptors, matches);
113 printf(
"%d: all matches size=%zd\n", imgId, matches.size());
114 std::string allMatchIdString{
"all matches "};
115 allMatchIdString += toString(imgId-1) +
"<->" + toString(imgId);
119 double bestRatio = 0.8;
120 std::sort(matches.begin(), matches.end());
121 matches.resize(
int(bestRatio * matches.size()));
122 printf(
"%d: best matches size=%zd\n", imgId, matches.size());
123 std::string bestMatchIdString{
"best " + toString(bestRatio) +
" matches "};
124 bestMatchIdString += toString(imgId-1) +
"<->" + toString(imgId);
128 prevImgGray = imgGray;
129 prevKeypoints = keypoints;
130 prevDescriptors = descriptors;
void sort(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int flags)
Sorts each row or each column of a matrix.
void cvtColor(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int code, int dstCn=0)
Converts an image from one color space to another.
Definition: videoio_c.h:169
_Tp width
the width
Definition: types.hpp:335
Definition: affine.hpp:51
static void showImage(cv::InputArray img, impl::CallMetaData metaData=impl::CallMetaData(), const char *description=nullptr, const char *view=nullptr)
Add a single image to debug GUI (similar to imshow <>).
Definition: show_image.hpp:38
Designed for command line parsing.
Definition: utility.hpp:799
Class for video capturing from video files, image sequences or cameras.
Definition: videoio.hpp:606
Template class for specifying the size of an image or rectangle.
Definition: types.hpp:315
void finalShow()
Passes the control to the debug-window for a last time.
Definition: final_show.hpp:23
void match(InputArray queryDescriptors, InputArray trainDescriptors, std::vector< DMatch > &matches, InputArray mask=noArray()) const
Finds the best match for each descriptor from a query set.
Brute-force descriptor matcher.
Definition: features2d.hpp:1078
InputOutputArray noArray()
static void debugFilter(cv::InputArray original, cv::InputArray result, impl::CallMetaData metaData=impl::CallMetaData(), const char *description=nullptr, const char *view=nullptr)
Use the debug-framework to compare two images (from which the second is intended to be the result of ...
Definition: filter.hpp:36
Definition: videoio_c.h:170
Definition: types_c.h:121
static void debugDMatch(cv::InputArray img1, std::vector< cv::KeyPoint > keypoints1, cv::InputArray img2, std::vector< cv::KeyPoint > keypoints2, std::vector< cv::DMatch > matches, const impl::CallMetaData &data, const char *description=nullptr, const char *view=nullptr, bool useTrainDescriptor=true)
Add a filled in DMatch <dmatch> to debug GUI.
Definition: dmatch.hpp:49
_Tp height
the height
Definition: types.hpp:336
Template class for smart pointers with shared ownership.
Definition: cvstd.hpp:261
Size2i Size
Definition: types.hpp:343
virtual void detectAndCompute(InputArray image, InputArray mask, std::vector< KeyPoint > &keypoints, OutputArray descriptors, bool useProvidedKeypoints=false)
n-dimensional dense array class
Definition: mat.hpp:771
bool empty() const
Returns true if the array has no elements.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(cvvisual_test)
SET(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH ~/software/opencv/install)
SET(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "g++-4.8")
SET(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O2 -pthread -Wall -Werror")
# (un)set: cmake -DCVV_DEBUG_MODE=OFF ..
OPTION(CVV_DEBUG_MODE "cvvisual-debug-mode" ON)
if(CVV_DEBUG_MODE MATCHES ON)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -DCVVISUAL_DEBUGMODE")
endif()
FIND_PACKAGE(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(cvvt main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(cvvt
opencv_core opencv_videoio opencv_imgproc opencv_features2d
opencv_cvv
)
- We compile the program either using the above CmakeLists.txt with Option CVV_DEBUG_MODE=ON (cmake -DCVV_DEBUG_MODE=ON) or by adding the corresponding define CVVISUAL_DEBUGMODE to our compiler (e.g. g++ -DCVVISUAL_DEBUGMODE).
The first cvv call simply shows the image (similar to imshow) with the imgIdString as comment.
The image is added to the overview tab in the visual debug GUI and the cvv call blocks.
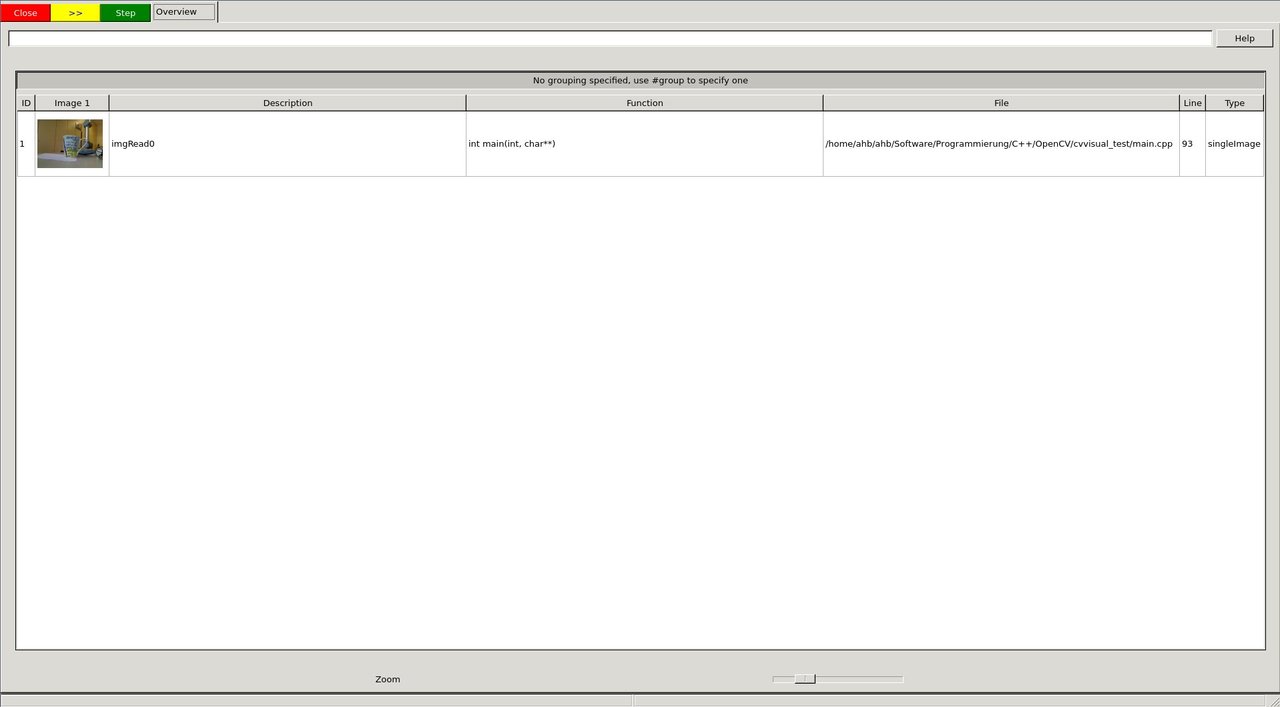
image
The image can then be selected and viewed
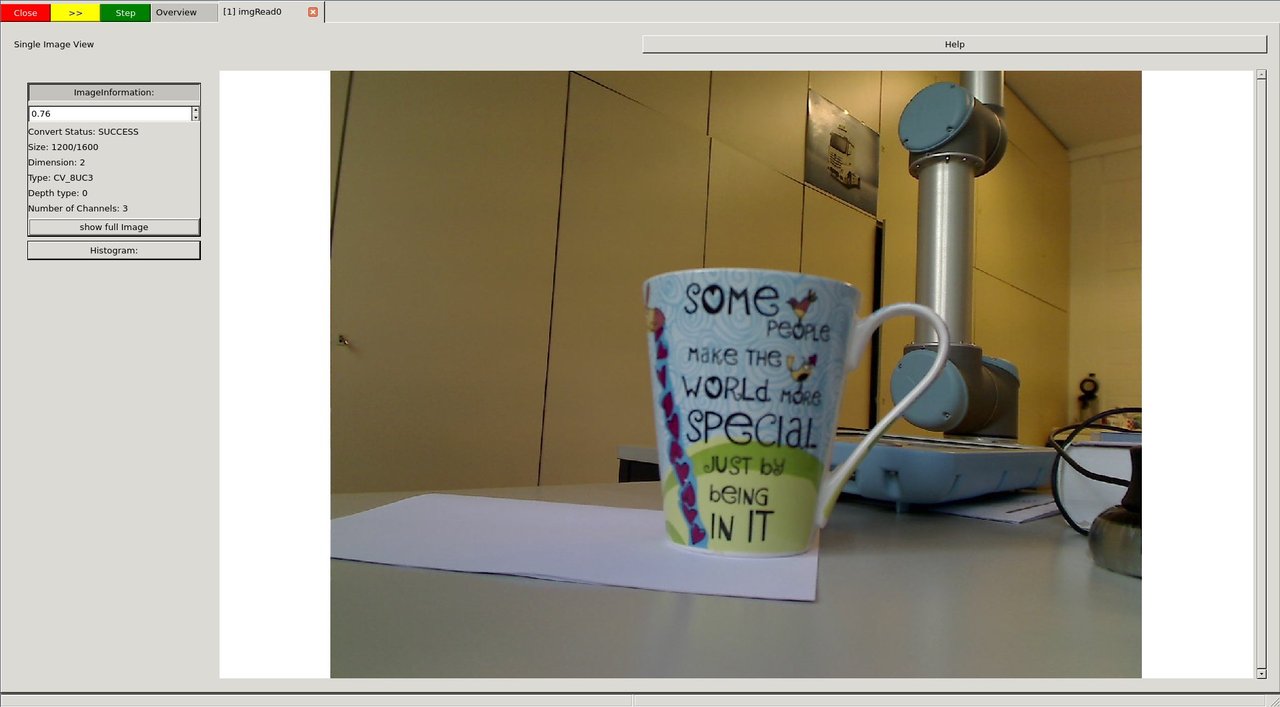
image
Whenever you want to continue in the code, i.e. unblock the cvv call, you can either continue until the next cvv call (Step), continue until the last cvv call (*>>*) or run the application until it exists (Close).
We decide to press the green Step button.
The next cvv calls are used to debug all kinds of filter operations, i.e. operations that take a picture as input and return a picture as output.
As with every cvv call, you first end up in the overview.
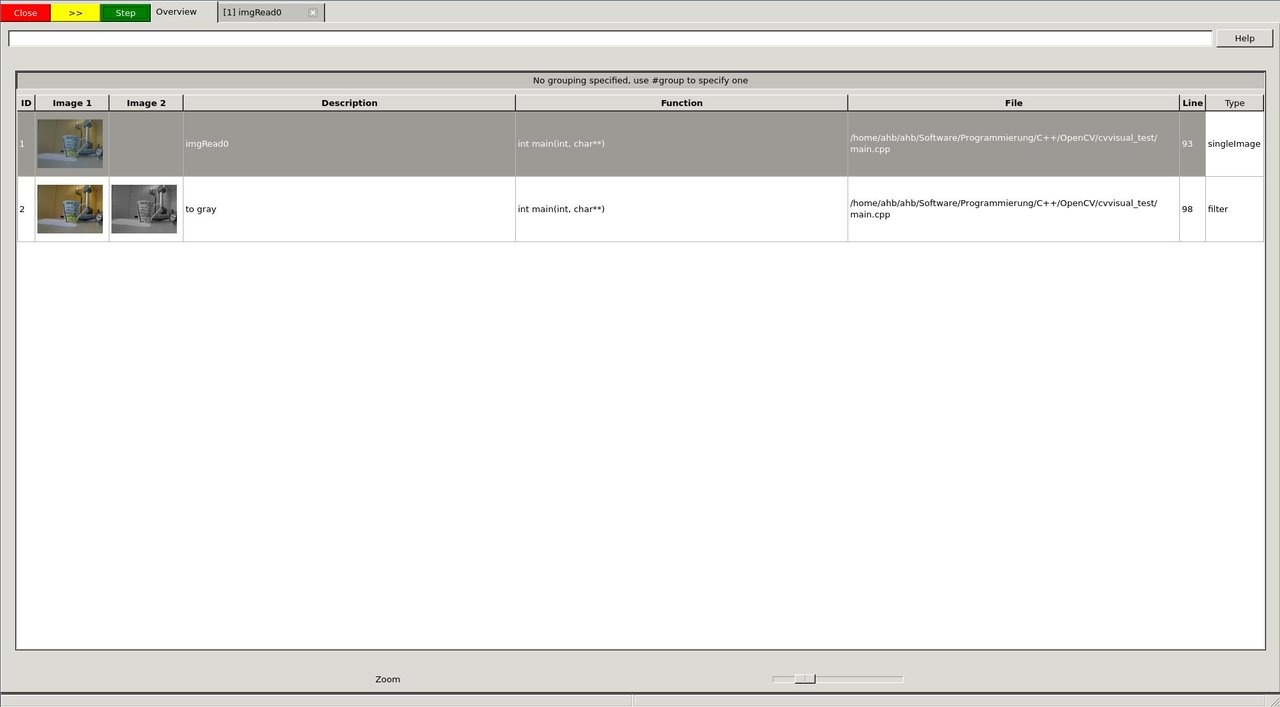
image
We decide not to care about the conversion to gray scale and press Step.
If you open the filter call, you will end up in the so called "DefaultFilterView". Both images are shown next to each other and you can (synchronized) zoom into them.
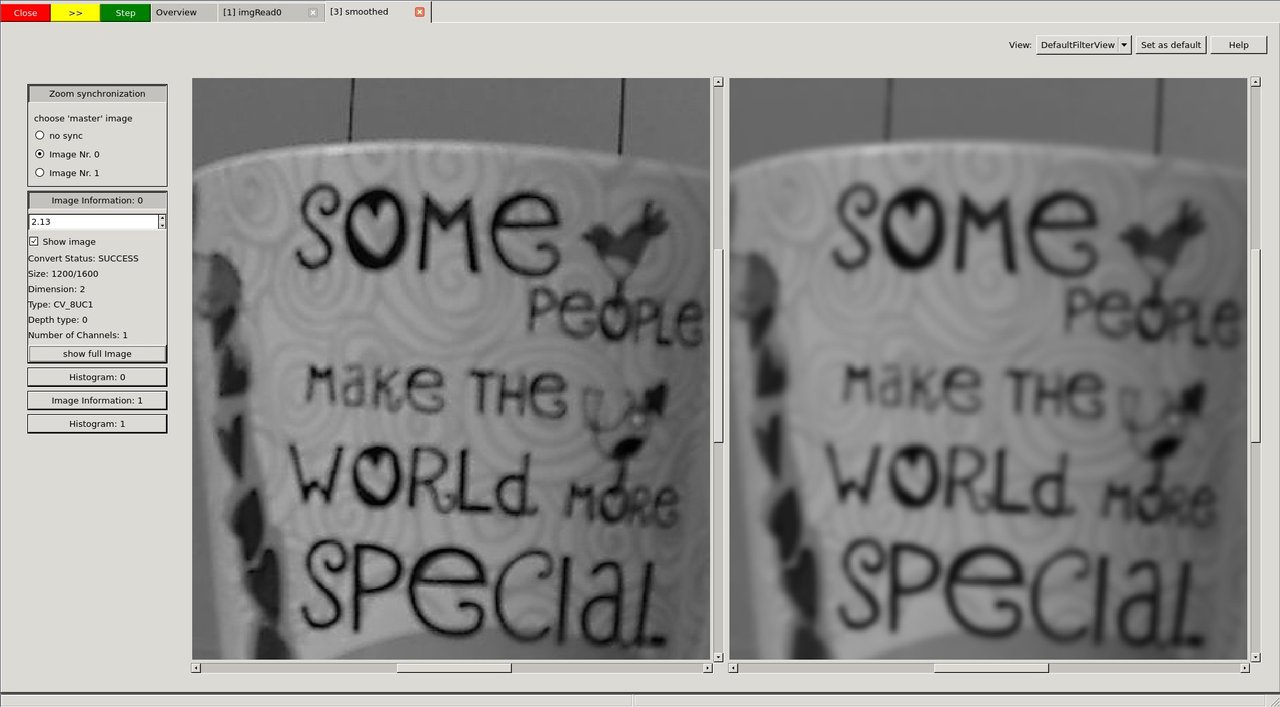
image
When you go to very high zoom levels, each pixel is annotated with its numeric values.
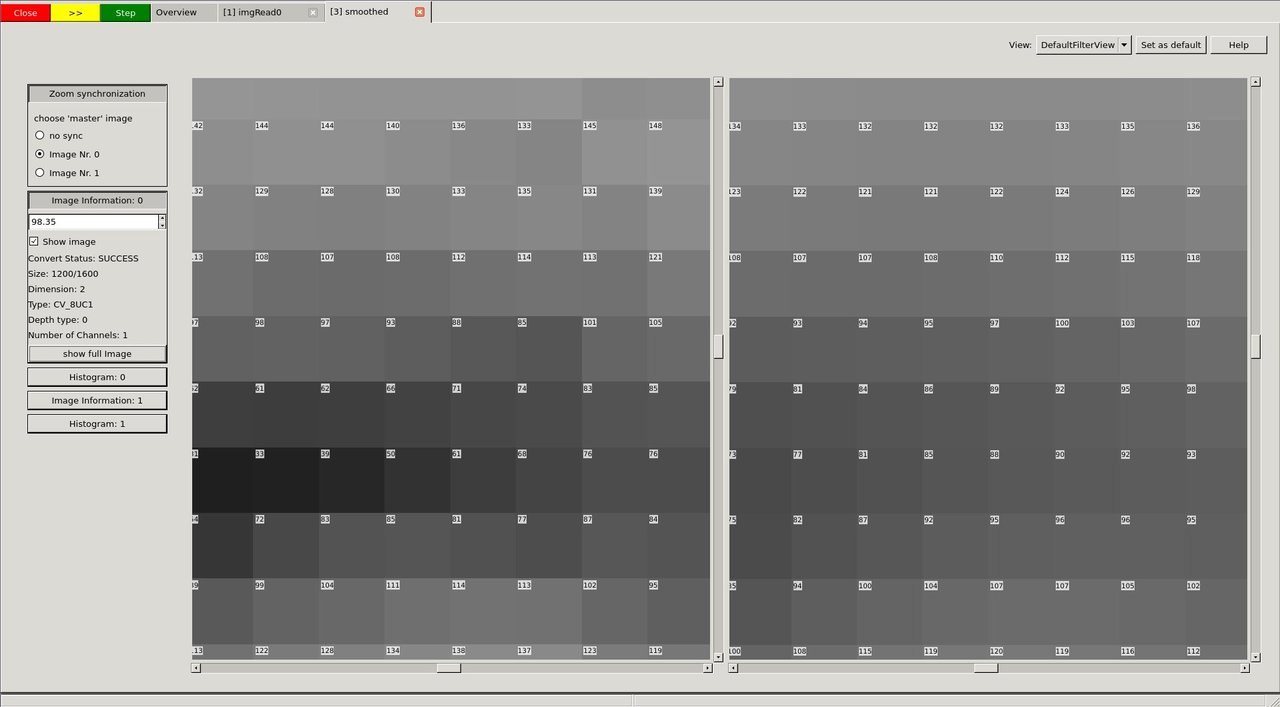
image
We press Step twice and have a look at the dilated image.
The DefaultFilterView showing both images
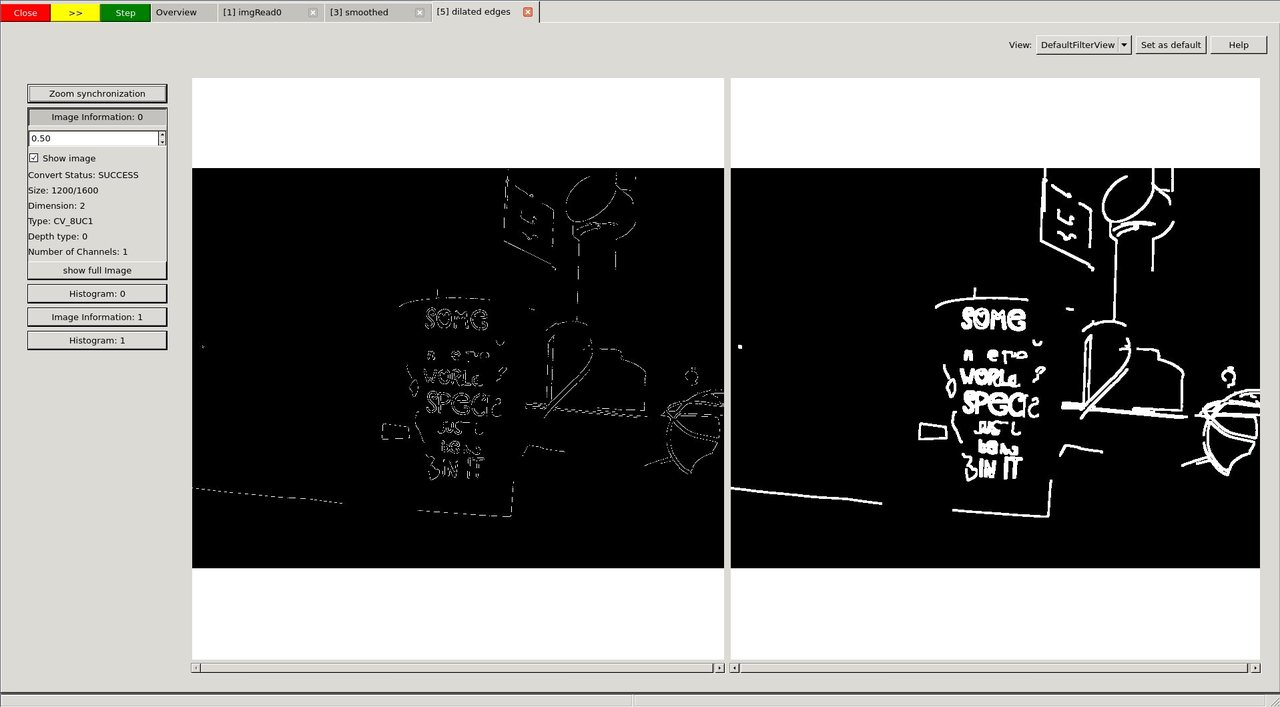
image
Now we use the View selector in the top right and select the "DualFilterView". We select "Changed Pixels" as filter and apply it (middle image).
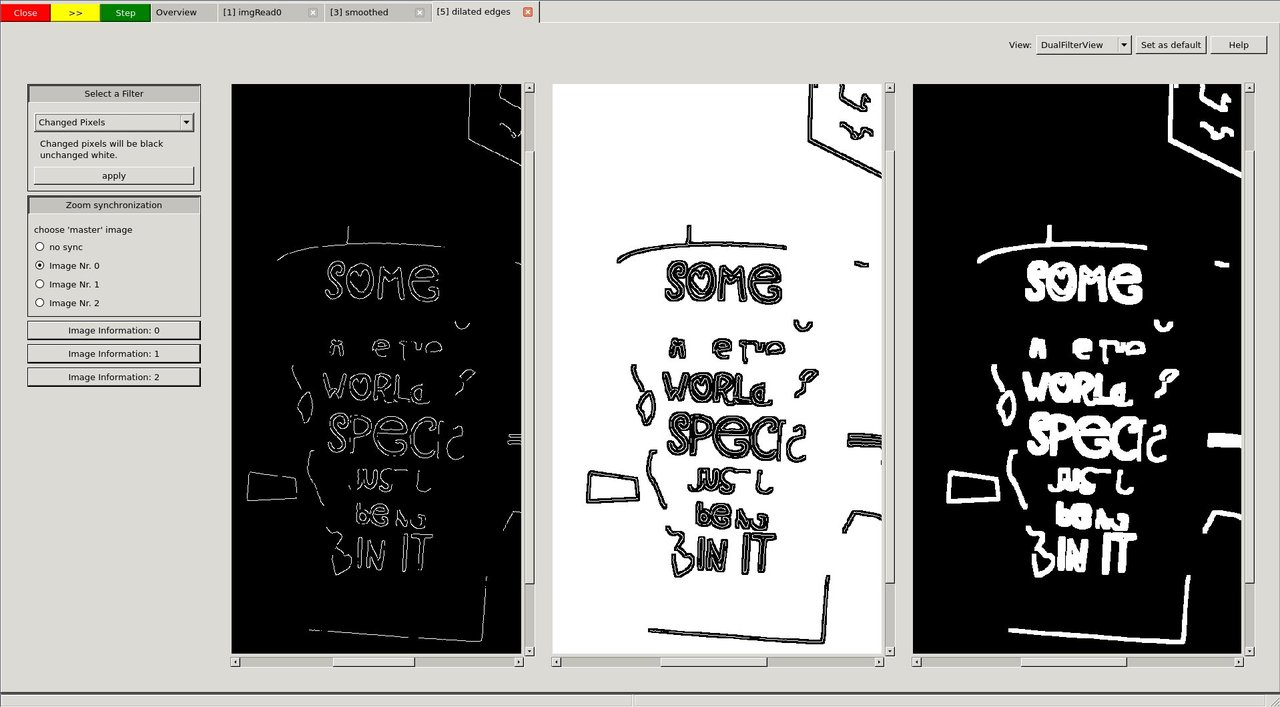
image
After we had a close look at these images, perhaps using different views, filters or other GUI features, we decide to let the program run through. Therefore we press the yellow *>>* button.
The program will block at
and display the overview with everything that was passed to cvv in the meantime.
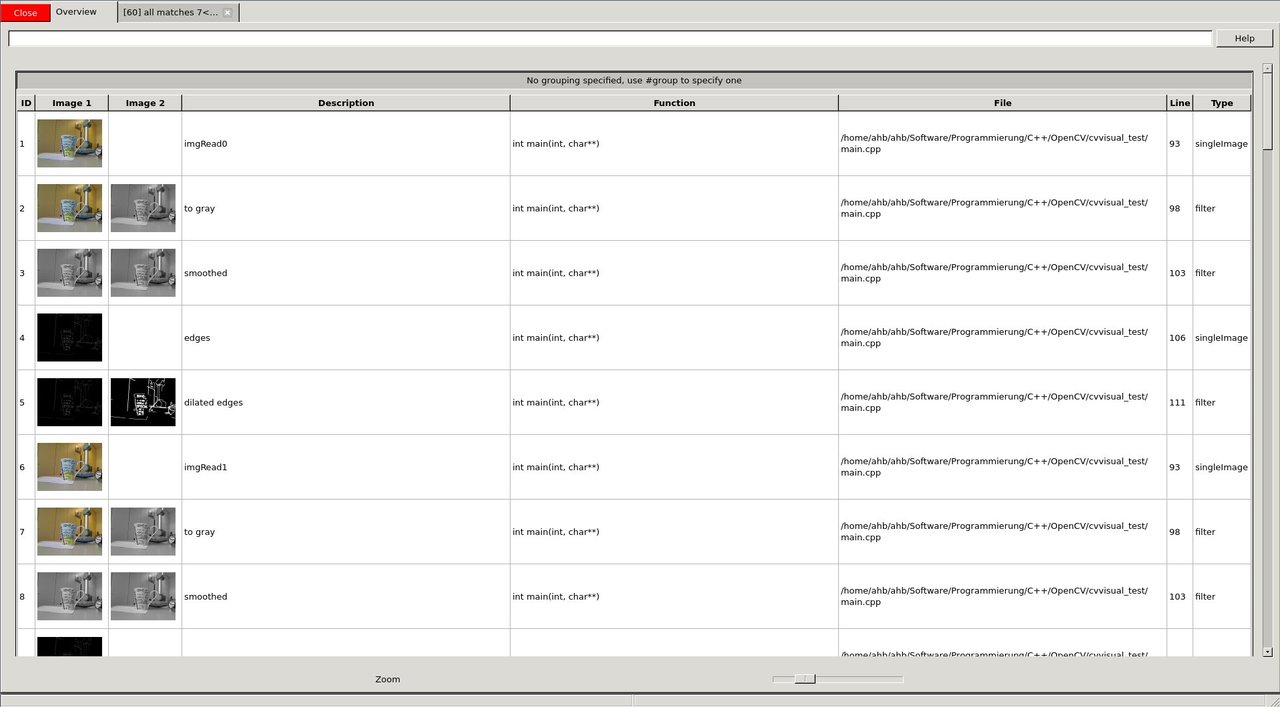
image
The cvv debugDMatch call is used in a situation where there are two images each with a set of descriptors that are matched to each other.
We pass both images, both sets of keypoints and their matching to the visual debug module.
Since we want to have a look at matches, we use the filter capabilities (*#type match*) in the overview to only show match calls.
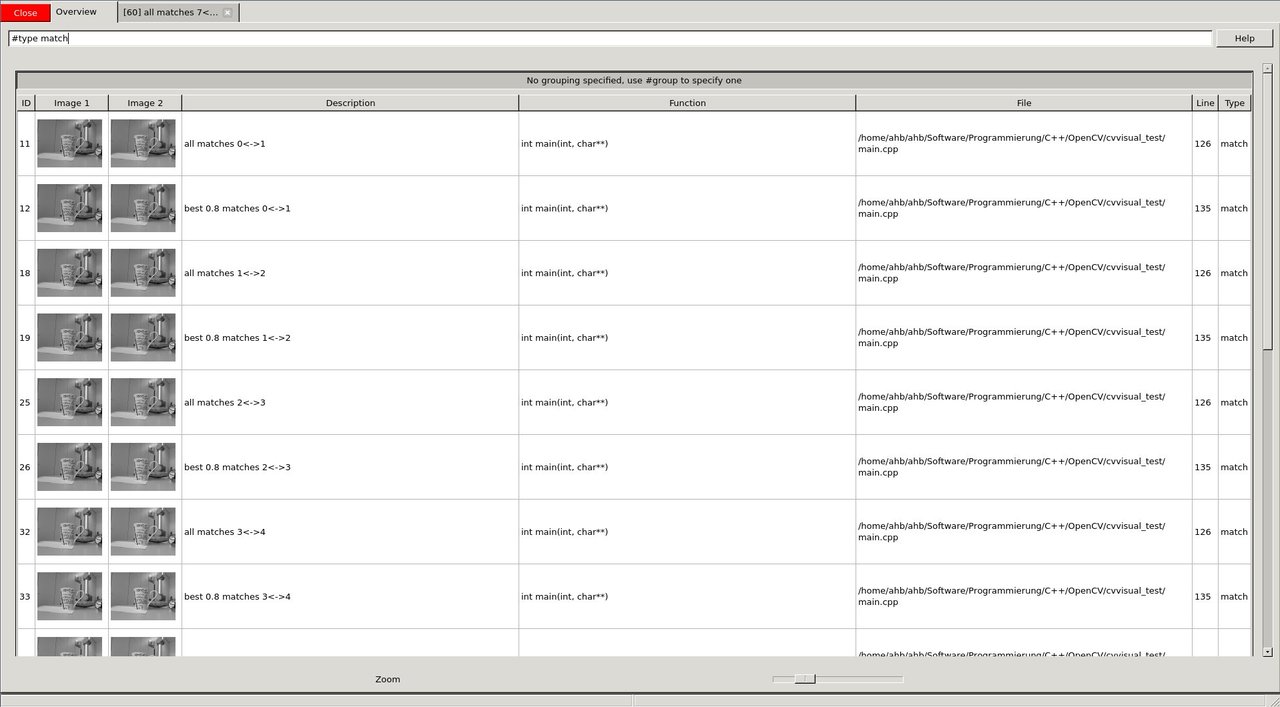
image
We want to have a closer look at one of them, e.g. to tune our parameters that use the matching. The view has various settings how to display keypoints and matches. Furthermore, there is a mouseover tooltip.
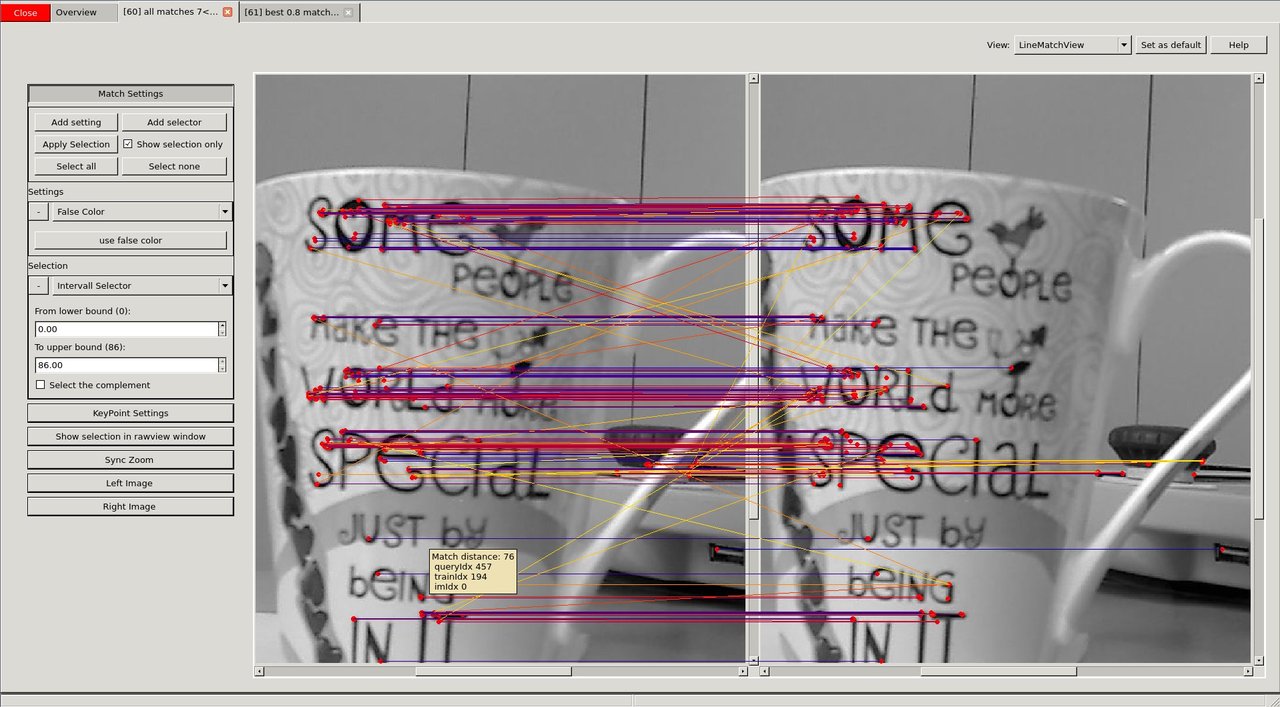
image
We see (visual debugging!) that there are many bad matches. We decide that only 70% of the matches should be shown - those 70% with the lowest match distance.
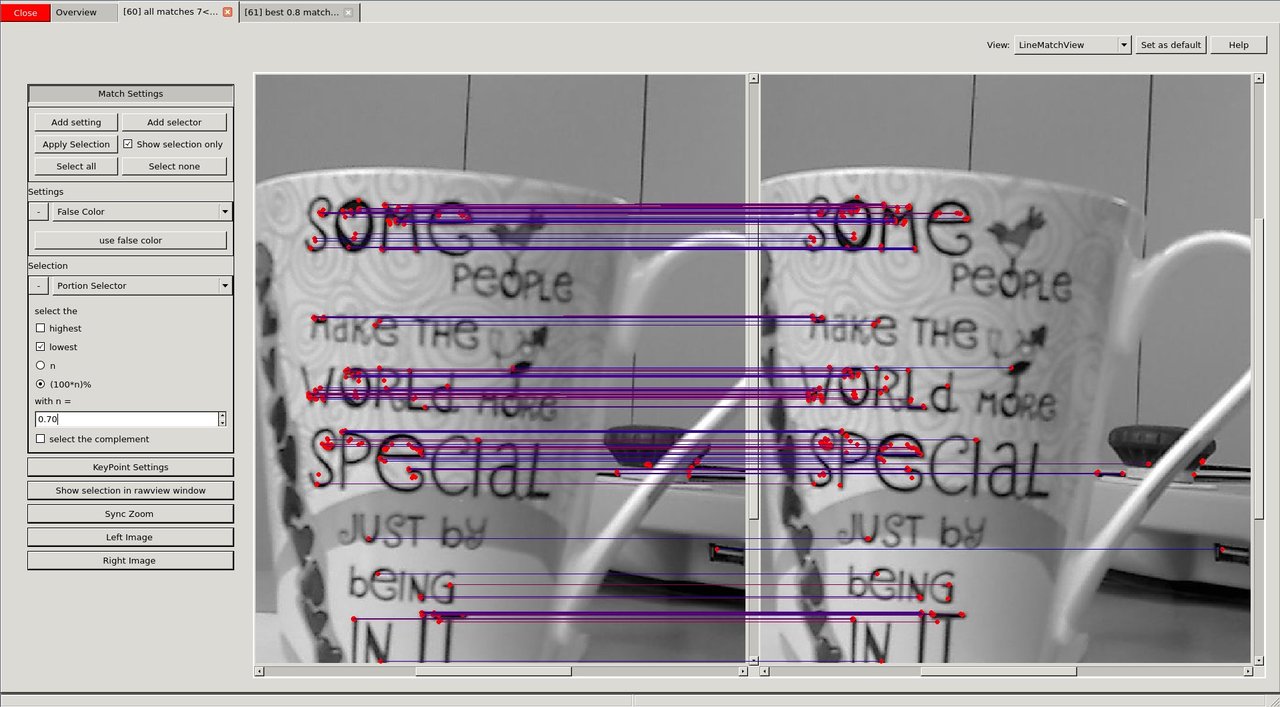
image
Having successfully reduced the visual distraction, we want to see more clearly what changed between the two images. We select the "TranslationMatchView" that shows to where the keypoint was matched in a different way.
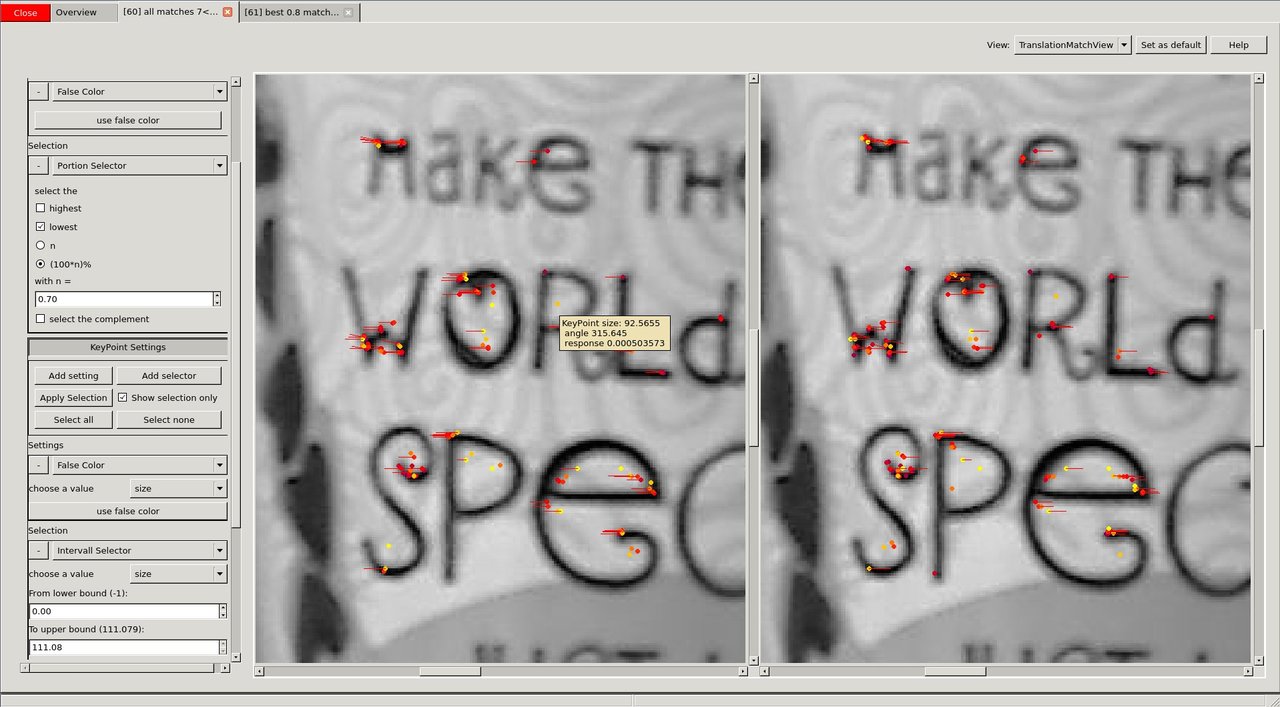
image
It is easy to see that the cup was moved to the left during the two images.
Although, cvv is all about interactively seeing the computer vision bugs, this is complemented by a "RawView" that allows to have a look at the underlying numeric data.
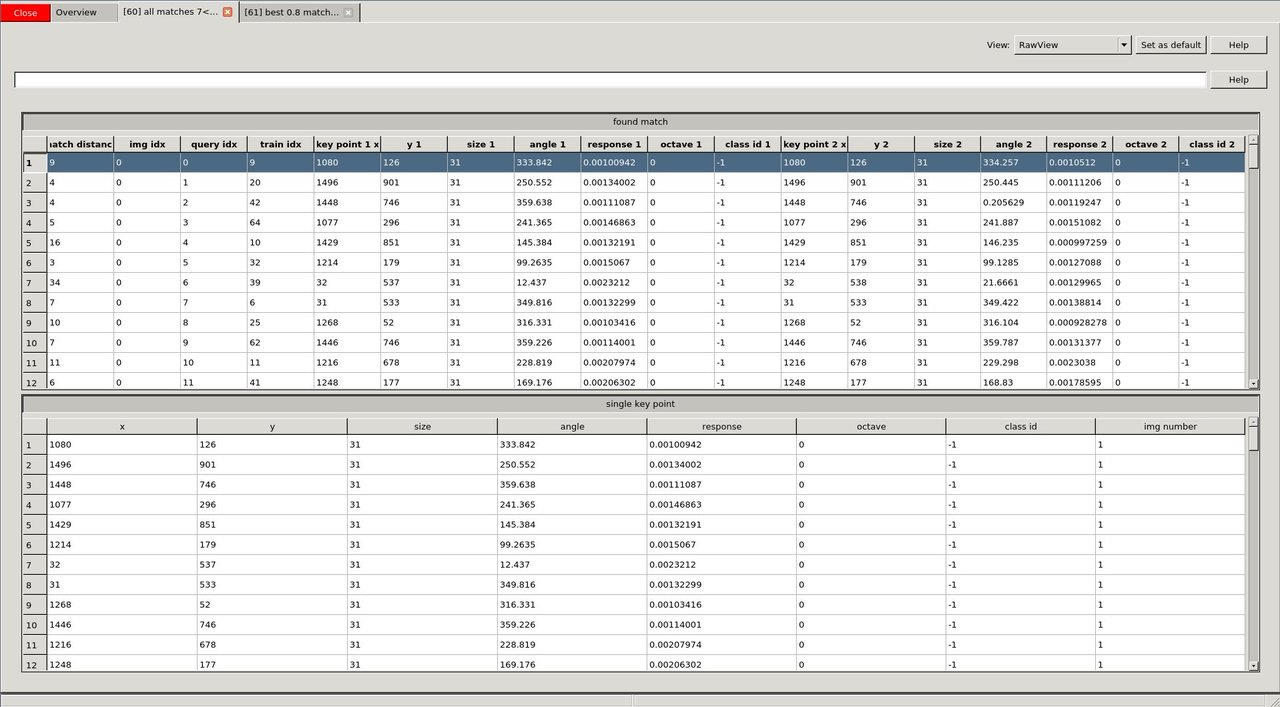
image
There are many more useful features contained in the cvv GUI. For instance, one can group the overview tab.
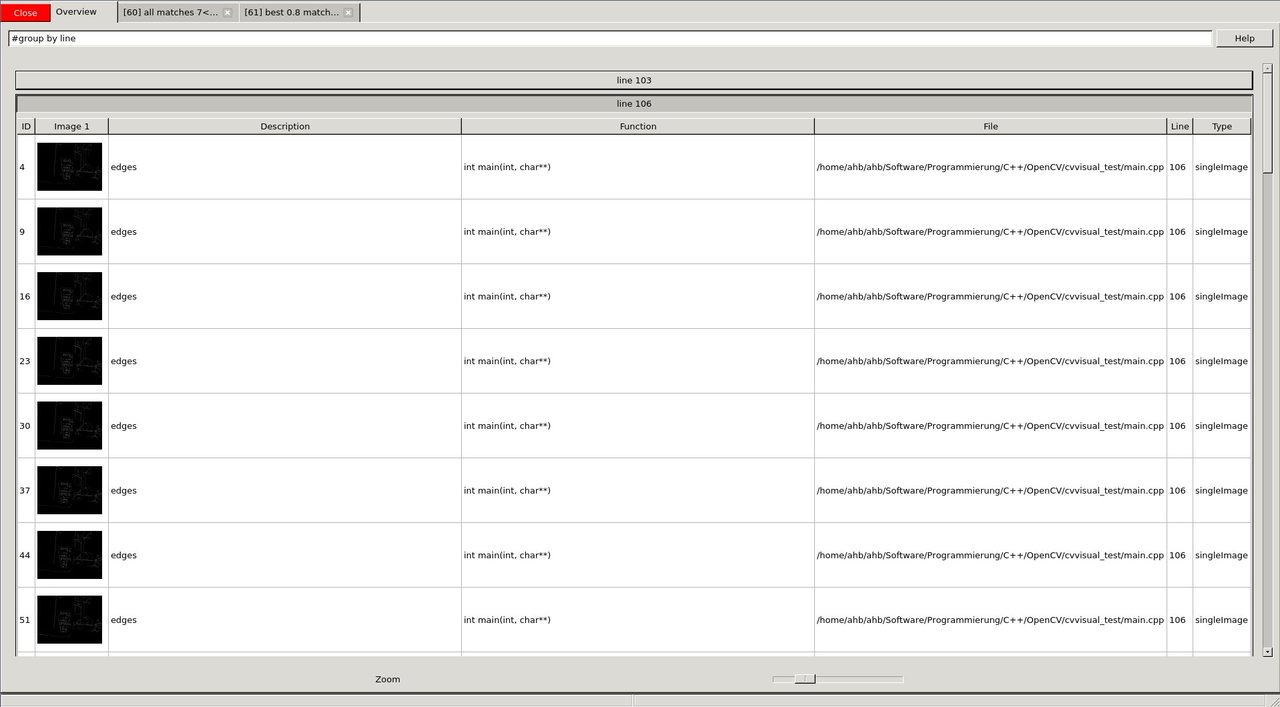
image
Result















 1.8.12
1.8.12